6.4 Resource access authentication and authorization context
A node is able to perform network layer communication once it has been authenticated and authorized to join the network. However, application layer authentication and authorization MAY be required before clients and servers can exchange application layer messaging. Registration (see 6.9) with a utility or third party service provider MAY also be needed to provide explicit device and user authorization at the application layer.
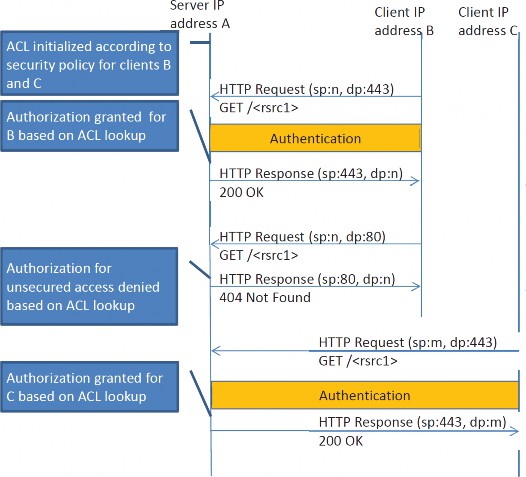
Resource access requiring application layer authentication, data confidentiality, and integrity checking SHALL occur through requests from a client to the server using HTTP over TLS (IETF RFC 2818) (also known as HTTPS) using TLS version 1.2 (IETF RFC 5246). Resource access not requiring application layer authentication, data confidentiality, or integrity checking SHALL occur through requests from a client to the host server using HTTP (IETF RFC 7230).
If a request is made to the port associated with HTTPS, it is considered an HTTPS request and authentication SHALL have taken place. If authentication has not taken place, authentication SHALL be initiated as described in 6.5. When authenticated, the request is then passed to the ACL associated with the resource. Ancillary information about the request obtained from the secure session, notably the level of client authentication, will also be compared with the ACL.
Authorization on a request-by-request basis is determined by the ACL settings for the resource, which may be set up at the end of the authentication based on the level of client authentication. The Local Registration List (aclLocalRegistrationList) may be additionally used to authorize on a device-by-device basis.

Figure 1 —Example device authentication procedure using HTTPS port 443